What is an orthopedic implant and how does it work?
orthopedic implants are crucial in modern medicine. They support and enhance the healing of bones and joints. In recent years, the orthopedic implant market has grown significantly, with a reported value of over $48 billion in 2021. This growth is largely driven by an aging population and increasing rates of musculoskeletal disorders.
Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading orthopedic surgeon, states, “Orthopedic implants can dramatically improve patient mobility and quality of life.” These devices, such as screws, plates, and prostheses, play a vital role in surgical procedures. They provide stability and enable proper alignment during the healing process. However, challenges persist in material durability and compatibility with the human body.
Despite advancements, complications can arise. Infections and implant failures remain areas needing attention. The industry faces pressures to innovate while ensuring patient safety. The journey of orthopedic implants is a testament to progress, yet the pursuit of perfection continues. As technology evolves, so too must our understanding of these essential devices.
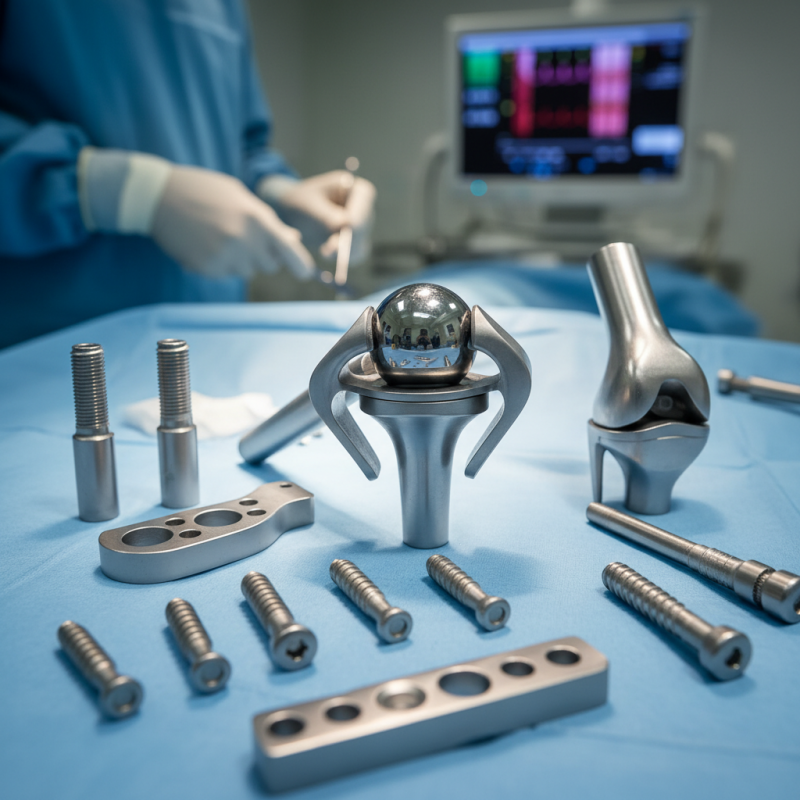
Definition of Orthopedic Implants and Their Purpose
Orthopedic implants are medical devices used to support bones and joints. They play a crucial role in surgeries involving fractures, joint replacements, and spinal issues. These implants can be made from various materials like metal, plastic, or ceramic, depending on the specific need. The design of each implant aims to replicate the natural function of the body, allowing for mobility and stability.
The primary purpose of orthopedic implants is to facilitate healing. They help secure broken bones, replace damaged joints, and assist in restoring functionality. For example, a knee implant provides a new surface for movement, reducing pain and improving quality of life. However, not all implants work as intended. Some may lead to complications, such as infection or rejection. The healing process can be unpredictable, making it essential to monitor each patient's response carefully.
Patients often face challenges after surgery. Pain management and rehabilitation are vital for recovery. Sometimes, the body may not accept the implant fully. This can lead to discomfort or further interventions. Therefore, the journey with orthopedic implants involves careful consideration and ongoing assessment to ensure the best outcomes.
Usage of Orthopedic Implants by Type (2023)
This chart displays the distribution of orthopedic implant types utilized in 2023, highlighting the most common categories used in medical procedures.
Types of Orthopedic Implants and Their Applications
Orthopedic implants are crucial in modern medicine. They help restore function and alleviate pain in injured joints and bones. Various types of implants are utilized based on specific needs. For instance, screws and plates provide stability to fractured bones. These devices are often made from titanium or stainless steel. Their compatibility with human tissue makes them effective.
Joint replacements are another common application. These implants replace damaged joints, offering pain relief. Materials used here include ceramics and polymers. They mimic the natural movement of joints well. However, complications can arise. Improper alignment during surgery can lead to persistent pain.
Fixation devices, like rods and nails, support broken bones during healing. They ensure proper alignment. Yet, these implants sometimes require removal later on. The recovery process varies and can be long. Monitoring the implant's performance over time is essential. Some patients may experience discomfort as they adjust. Continuous follow-up is necessary to address any arising issues.
Materials Used in Orthopedic Implants
Orthopedic implants play a crucial role in modern medicine. They are used to support damaged bones and joints. The choice of materials in these implants is critical for their longevity and effectiveness. Common materials include titanium, cobalt-chromium alloys, and bioceramics. Each material has specific properties that suit different applications.
Titanium is lightweight yet strong. It is also biocompatible, reducing the risk of rejection. About 45% of orthopedic implants are made from titanium. Cobalt-chromium alloys offer excellent wear resistance. These materials are often used in joint replacements. Bioceramics, on the other hand, promote bone growth. They are gaining popularity for their ability to bond with natural bone.
However, challenges remain. Corrosion can occur, especially in moist environments inside the body. Some materials can elicit inflammatory responses. These factors must be carefully considered during design. Continuous research is needed to improve material performance. Data shows that 20% of patients experience complications due to implant materials. Striking a balance between durability and biocompatibility is essential for future developments.
What is an orthopedic implant and how does it work? - Materials Used in Orthopedic Implants
| Material Type | Common Uses | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloys | Joint replacements, trauma pins | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to stainless steel |
| Stainless Steel | Fracture fixation, spinal implants | Cost-effective, good mechanical properties | Susceptible to corrosion |
| Polyethylene | Acetabular sockets in hip replacements | Good wear resistance, low friction | Limited load-bearing capacity |
| Ceramics | Hip prostheses, dental implants | Biocompatibility, excellent wear resistance | Brittleness, potential for fracture |
| Bioactive Glass | Bone graft materials, coatings | Promotes bone bonding, bioactive properties | Weaker mechanical properties than metals |
How Orthopedic Implants Work in the Body
Orthopedic implants are devices designed to support or replace damaged bone or joint structures. After surgery, these implants become integrated into the body. They help restore function and relieve pain. According to the Global Orthopedic Implant Market report, the industry is expected to reach $58 billion by 2025. This indicates the growing reliance on these technologies.
Once implanted, the body begins a healing response. Osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, are stimulated. They can surround the implant, creating a bond with the surrounding bone. This process is called osseointegration. However, it's not always perfect. Some patients may experience complications like implant loosening or infection. Data suggests that up to 10% of implants may fail within a decade, highlighting the challenges in this field.
Understanding how these devices work is crucial for both patients and professionals. Monitoring the integration process is essential. The right balance of materials and techniques can improve outcomes. Yet, the complexities of healing, such as individual biological responses, add uncertainty. The continuous advancements in implant technology aim to reduce these risks but require ongoing research.
Factors Influencing the Success of Orthopedic Implants
Orthopedic implants play a pivotal role in modern medicine. Their effectiveness can be influenced by various factors that deserve attention. One key factor is the patient's overall health. Conditions like diabetes or obesity can slow recovery. Doctors must evaluate these issues before surgery.
Another important element is the type of material used in the implant. Metals like titanium are popular for their strength. However, the body may react differently to various materials. Some patients experience discomfort, which can complicate recovery.
The skill of the surgeon is equally vital. A well-performed procedure can greatly enhance success rates.
Post-operative care also matters. Physical therapy, for instance, can accelerate healing. Patients must be committed to their recovery program. Yet, some skip sessions, hindering progress. Awareness of these factors can lead to better outcomes with orthopedic implants. Users often need guidance on what to expect.
